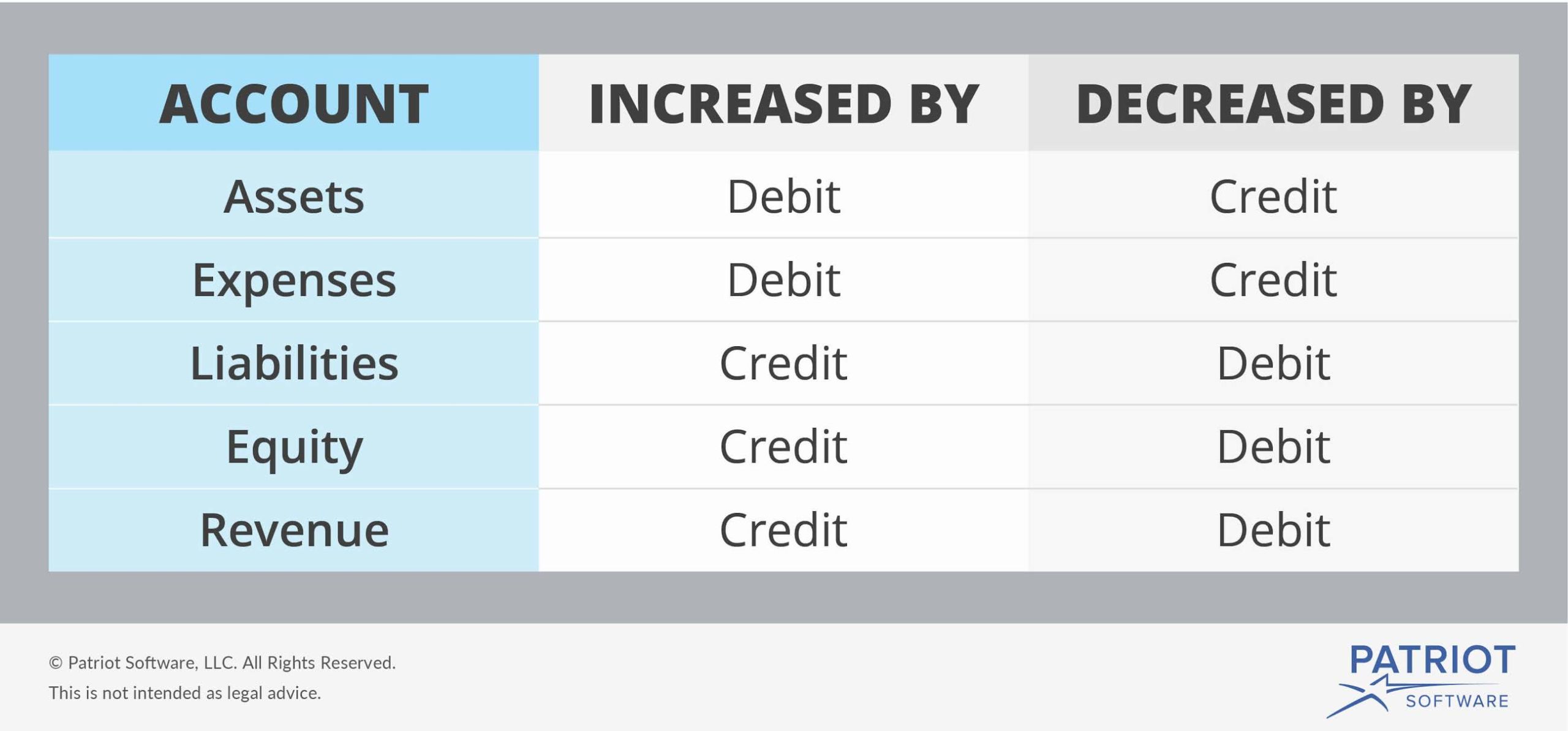
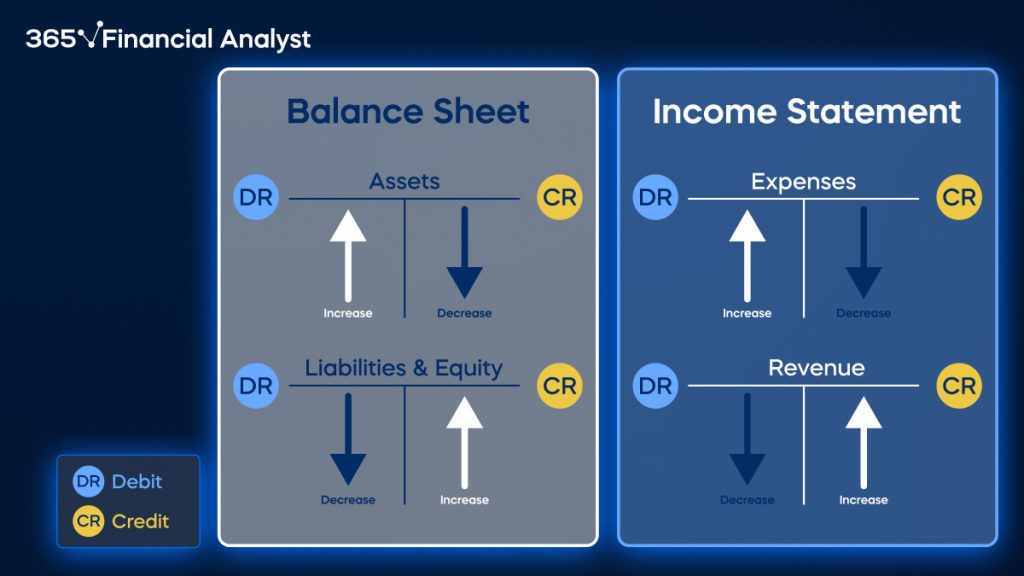
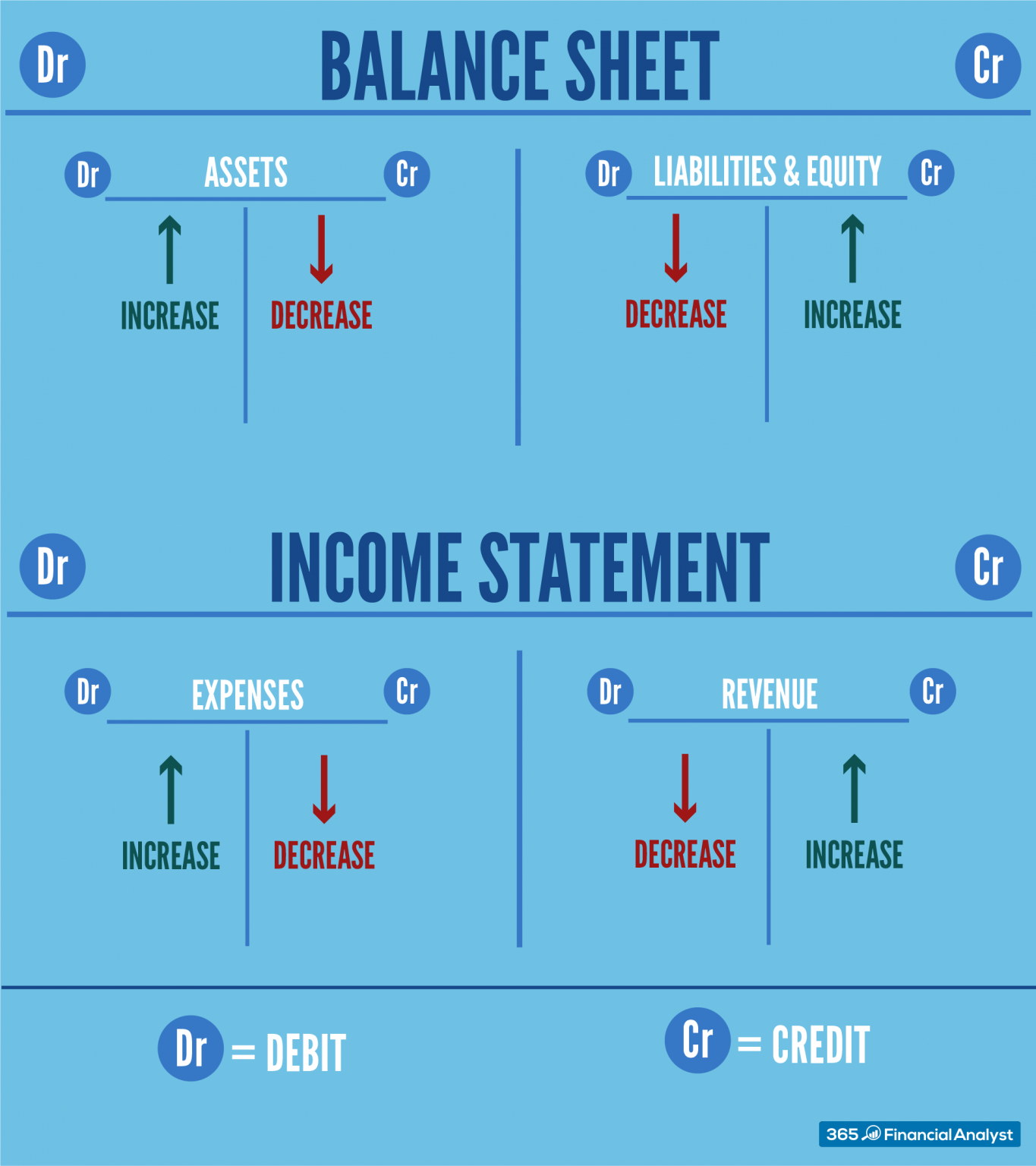
Accounting Debit Credit Cheat Sheet - Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate The cardinal rule of bookkeeping is that debits. It also includes a debits and credits. Use the cheat sheet in this article to get to grips with how credits and debits affect your accounts. While assets, liabilities and equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are the increases and decreases made to the various accounts whenever a financial transaction occurs. As a general rule, if a debit increases 1 type of account, a credit will decrease it. For easy reference the chart below shows the effect of debits and credits on particular types of account. Credits go on the right, and they either increase or decrease accounts depending on the type of. This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation.
For easy reference the chart below shows the effect of debits and credits on particular types of account. This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation. The cardinal rule of bookkeeping is that debits. Credits go on the right, and they either increase or decrease accounts depending on the type of. As a general rule, if a debit increases 1 type of account, a credit will decrease it. Use the cheat sheet in this article to get to grips with how credits and debits affect your accounts. It also includes a debits and credits. While assets, liabilities and equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are the increases and decreases made to the various accounts whenever a financial transaction occurs. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate
Credits go on the right, and they either increase or decrease accounts depending on the type of. As a general rule, if a debit increases 1 type of account, a credit will decrease it. Use the cheat sheet in this article to get to grips with how credits and debits affect your accounts. The cardinal rule of bookkeeping is that debits. It also includes a debits and credits. While assets, liabilities and equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are the increases and decreases made to the various accounts whenever a financial transaction occurs. For easy reference the chart below shows the effect of debits and credits on particular types of account. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
Use the cheat sheet in this article to get to grips with how credits and debits affect your accounts. As a general rule, if a debit increases 1 type of account, a credit will decrease it. For easy reference the chart below shows the effect of debits and credits on particular types of account. It also includes a debits and.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate Use the cheat sheet in this article to get to grips with how credits and debits affect your accounts. While assets, liabilities and equity are types.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified.
Debit And Credit Cheat Sheet Chart of Debits and Credits Accounting
For easy reference the chart below shows the effect of debits and credits on particular types of account. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate As a general rule, if a debit increases.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
While assets, liabilities and equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are the increases and decreases made to the various accounts whenever a financial transaction occurs. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
Credits go on the right, and they either increase or decrease accounts depending on the type of. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate For easy reference the chart below shows the effect.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to.
Debits and Credits Cheat Sheet 365 Financial Analyst
Credits go on the right, and they either increase or decrease accounts depending on the type of. This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on.
Debits and Credits Cheat Sheet 365 Financial Analyst
This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation. As a general rule, if a debit increases 1 type of account, a credit will decrease it. While assets, liabilities and equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are.
Printable Debits And Credits Cheat Sheet
This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified.
The Cardinal Rule Of Bookkeeping Is That Debits.
Use the cheat sheet in this article to get to grips with how credits and debits affect your accounts. Debits and credits debit cash, credit asset, debit accumulated depreciation, debit loss on sale bonds financial instrument (agreement) issued by a company to borrow money from investors at a specified term (time) and rate It also includes a debits and credits. As a general rule, if a debit increases 1 type of account, a credit will decrease it.
For Easy Reference The Chart Below Shows The Effect Of Debits And Credits On Particular Types Of Account.
Credits go on the right, and they either increase or decrease accounts depending on the type of. This article helps you grasp the concepts by walking you through the meaning and applications of debit and credit in accounting and how they relate to the fundamental accounting equation. While assets, liabilities and equity are types of accounts, debits and credits are the increases and decreases made to the various accounts whenever a financial transaction occurs.