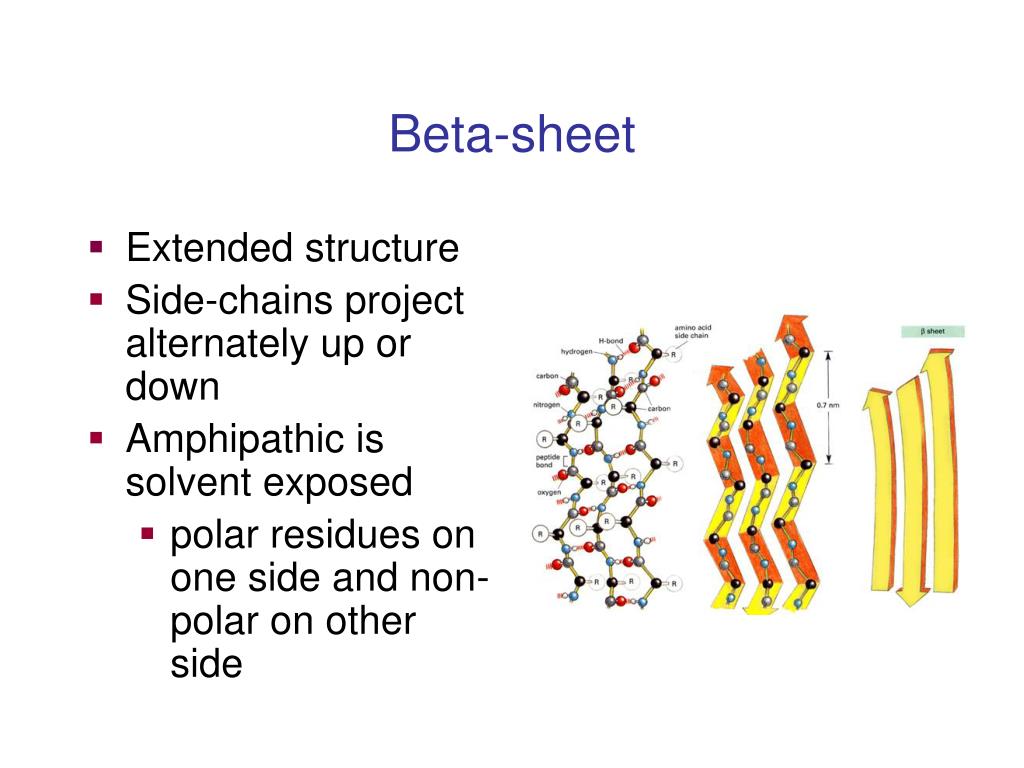
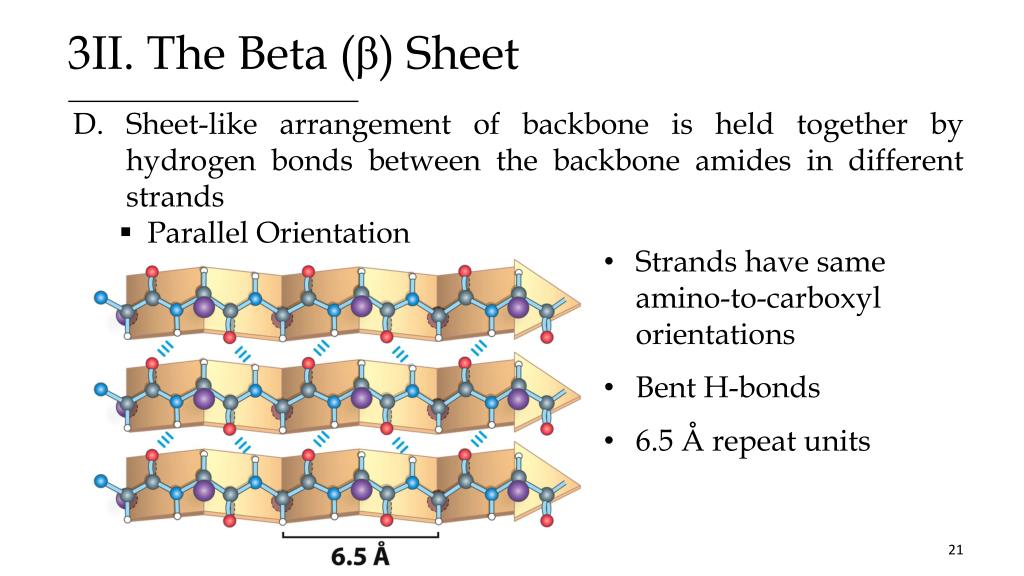
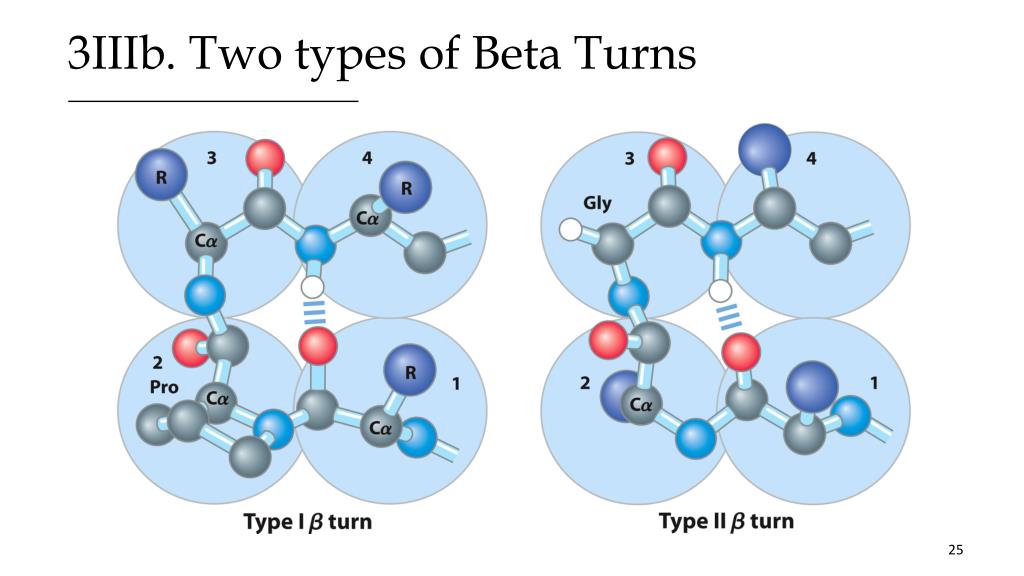
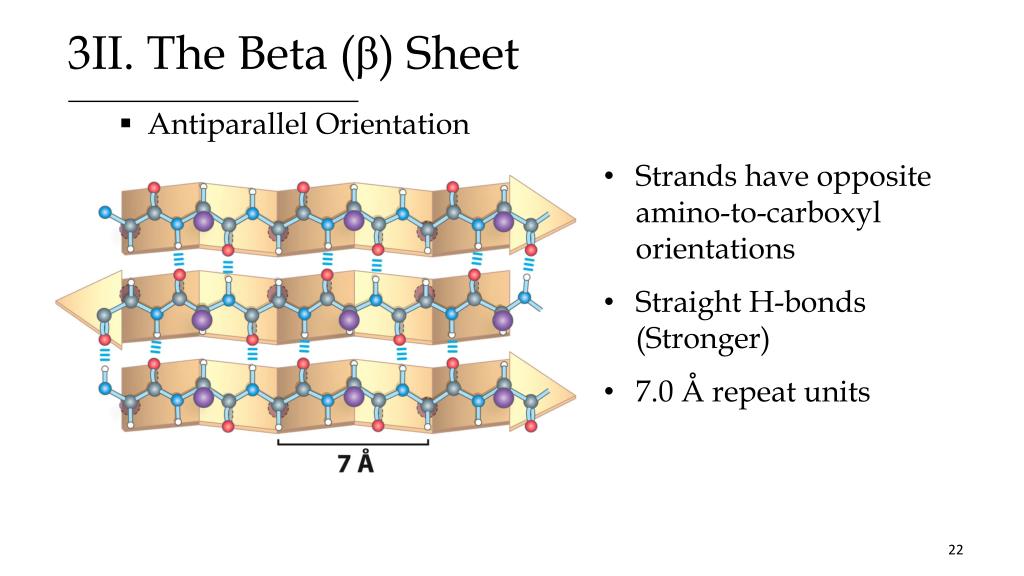
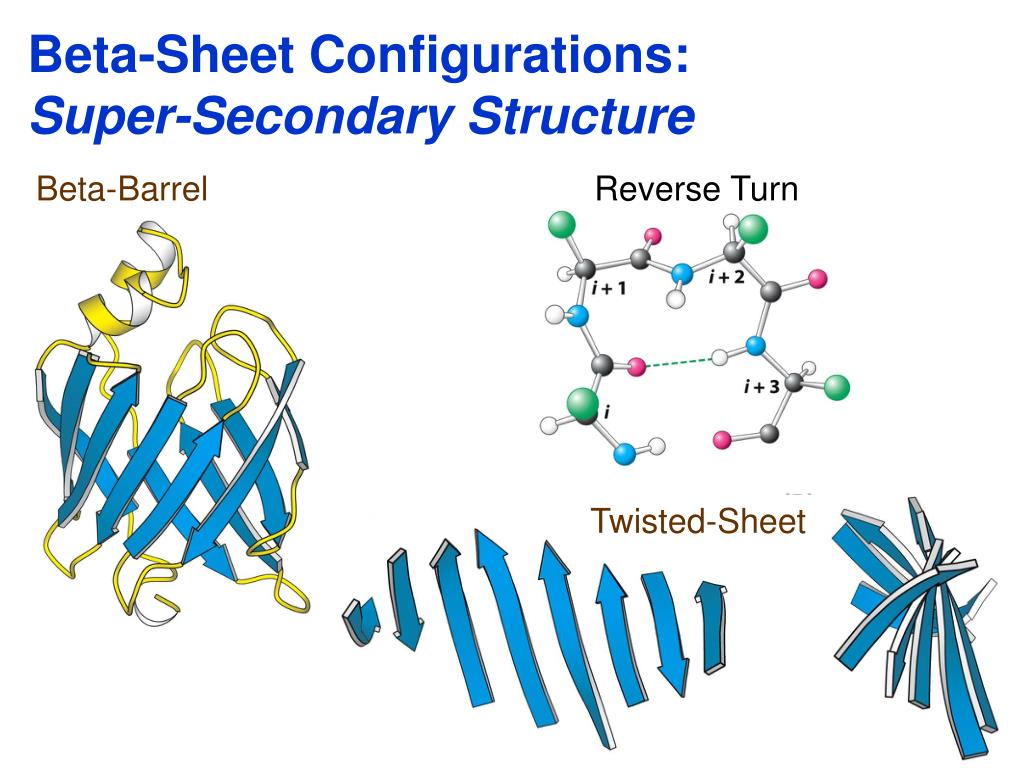
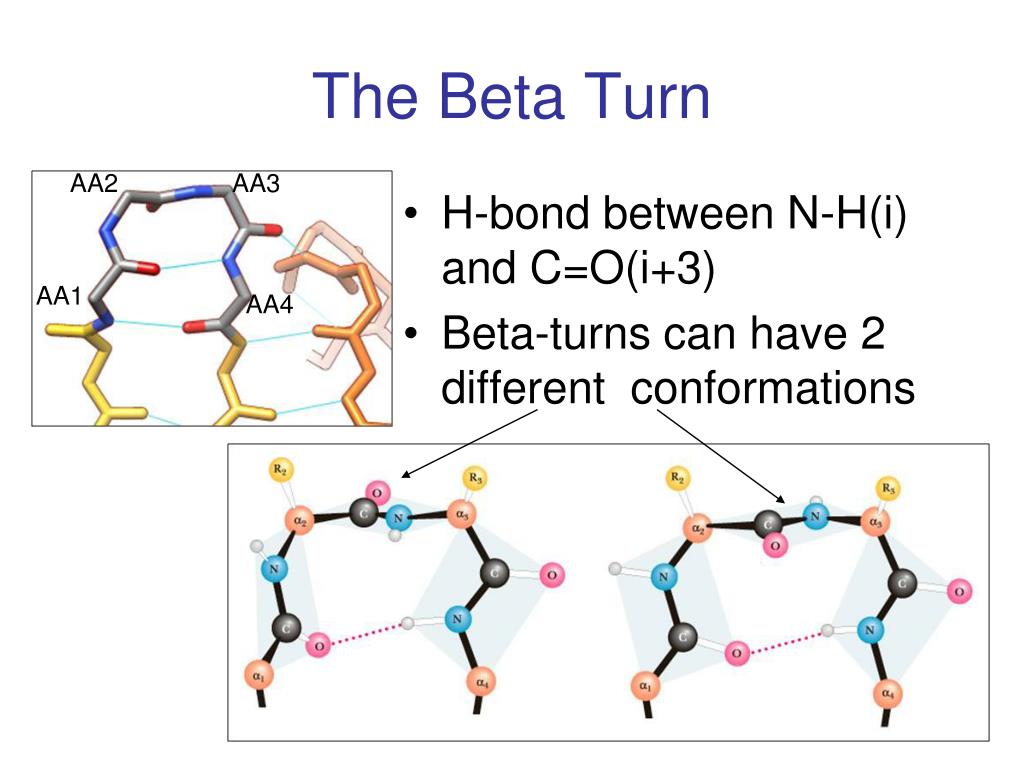
Beta Turn Vs Beta Sheet - The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. The secondary structure can allow.
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. The secondary structure can allow. The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn.
The secondary structure can allow. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to.
Levels of protein structure secondary Biomacromolecular structures
The secondary structure can allow. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. The use of i,.
PPT Protein Structure PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4519007
The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. The secondary structure can allow.
PPT Protein Structure Primary and Secondary Structure PowerPoint
The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. The secondary structure can allow. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and.
Amino Acid Secondary Structure
The secondary structure can allow. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and. The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin.
PPT Protein Structure Primary and Secondary Structure PowerPoint
The secondary structure can allow. The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn.
PPT Protein Structure Primary and Secondary Structure PowerPoint
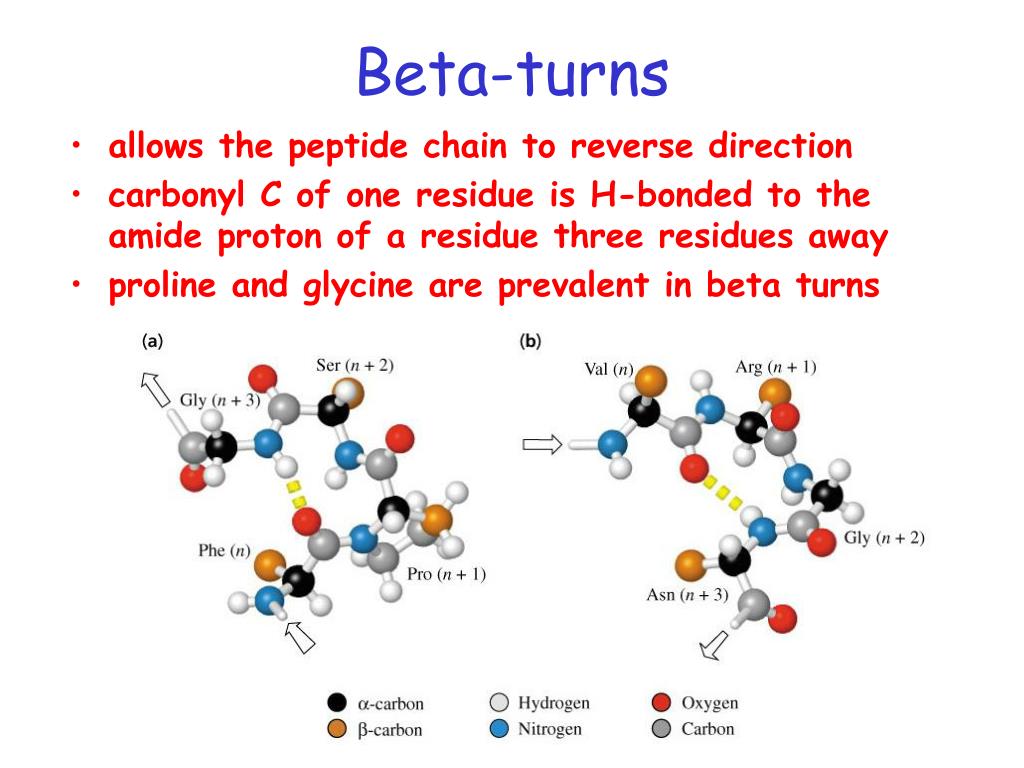
Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. The secondary structure can allow. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. Explain how beta strands.
PPT Proteins Amino Acid Chains PowerPoint Presentation, free
Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn..
PPT Biological Macromolecules PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. The secondary structure can allow. The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn.
PPT Protein Structure Databases PowerPoint Presentation, free
Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. The secondary structure can allow. Parallel beta sheets can't be connected with beta turns because the strand doesn't make a hairpin turn. Explain how beta strands.
PPT Chapter 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6788915
The type of beta turn displayed is generally related to the identity of the amino acids found in the turn. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to. Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes.
The Type Of Beta Turn Displayed Is Generally Related To The Identity Of The Amino Acids Found In The Turn.
The use of i, i+1, i+2, and i+3, are. It goes up and above the sheet, then loops. The secondary structure can allow. Short turns and longer loops are essential in protein 3d structures, connecting strands to.
Parallel Beta Sheets Can't Be Connected With Beta Turns Because The Strand Doesn't Make A Hairpin Turn.
Explain how beta strands form pleated sheet structures and how the alternating orientation of side chains contributes to sheet stability and.